Description
Country of Origin: Poland
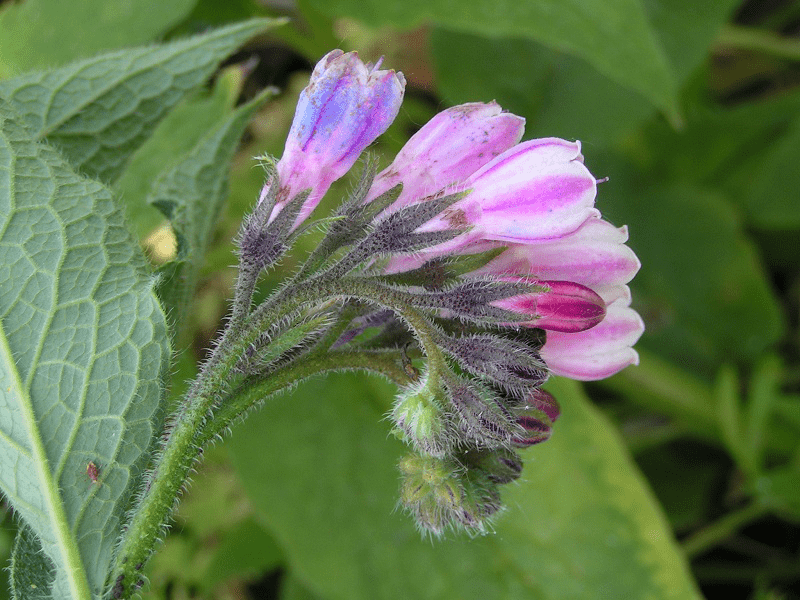
Comfrey (Symphytum officinale) also comphrey is a common name for plants in the genus Symphytum is a perennial herb of the family Boraginaceae with a black, turnip-like root and large, hairy broad leaves that bears small bell-shaped flowers of various colours, typically cream or purplish, which may be striped. It is native to Europe, growing in damp, grassy places, and is locally frequent throughout Ireland and Britain on river banks and ditches. The word comfrey is Latin in origin and means "to grow together.
Comfrey species are important herbs inorganic gardening. It is used as a fertilizer and as an herbal. The most commonly used species is Russian comfrey, which is a cross or hybrid of Symphytum officinale (common comfrey) and Symphytum asperum (rough comfrey).
Comfrey was historically used to treat a wide variety of ailments ranging from bronchial problems, broken bones, sprains, arthritis, gastric and varicose ulcers, severe burns, acne and other skin conditions. It was reputed to have bone and teeth building properties in children, and have value in treating "many female disorders".
Comfrey contains substances that help skin regrow, including allantoin, rosmarinic acid, and tannins. It also has poisonous chemicals called pyrrolizidine alkaloids.
Precautions
Comfrey has toxic substances that can cause severe liver damage and even death. You should never take comfrey by mouth.
The toxic substances in comfrey can be absorbed by the skin. Even creams and ointments should be used for only a short time, and only under a doctor's supervision.
DO NOT use comfrey on open wounds or broken skin.
DO NOT use comfrey if you have liver disease, alcoholism, or cancer.
Children, the elderly, and pregnant or breastfeeding women should not use comfrey products, even ones for the skin.